Return on capital employed (ROCE) is one of the most important financial tools used by businesses to assess their overall performance and progress. ROCE can provide companies with insight into whether they are using their capital effectively, allowing them to make smarter decisions on how to invest in future projects. However, many business owners don’t understand exactly what return on capital employed means or its importance within a broader operating strategy – this guide will explain everything you need to know about ROCE so that you can leverage it as an effective measure of success for your own organization.
What is Return on Capital Employed?
Return on Capital Employed (ROCE) is a profitability ratio that measures the return generated from capital employed in a business. It attempts to measure how efficiently a company uses its capital to generate profits and is calculated by dividing net operating profit by total capital employed. ROCE gives an indication of the financial performance of a company, as it indicates how much income is generated for each unit of capital invested.
A higher ROCE means more profit generated from the same amount of capital and vice versa. This ratio can be used by shareholders and investors to assess the company’s return on investment and make informed decisions about investing in it. It can also be used by analysts to compare companies within the same industry, as a higher ROCE usually indicates better performance.
Why Is It Important For Startups to track the Return on Capital Employed?
Following are the reasons why tracking the Return on Capital Employed is important for Startups:
1) It helps to track the progress of a business:
Tracking the Return on Capital Employed allows startups to see how their investments are performing, which can help them measure the progress of their company.
2) It provides insights into profitability:
Calculating and tracking this metric gives entrepreneurs an indication of how profitable their investments are. This can help them to make more informed decisions about their resources, such as whether or not to invest in a particular project.
3) It allows for better budgeting:
By understanding how much capital is needed to generate income, startups can budget accordingly and ensure that they are utilizing the most effective strategies for growth.
4) It helps to identify areas of improvement:
Tracking this metric can help entrepreneurs to identify areas of their business that need improvement, such as increasing sales or streamlining operations.
5) It helps to strategize:
By understanding the return on capital employed, startups can better plan and strategize for future investments. This will allow them to make more informed decisions about where and how to allocate resources in order to maximize returns.
Ultimately, tracking the Return on Capital Employed is an important tool for startups in order to monitor their investments and ensure that they are utilizing resources most effectively. It can also provide entrepreneurs with a better understanding of the overall financial health of their business, which is critical for long-term success.
How To Calculate the Return on Capital Employed?
Here is the formula to calculate the Return on Capital Employed:
Let’s look at an example to understand this better: Let’s say Company ABC has a NOPAT of $3,500 and Capital Employed of $20,000. To calculate its ROCE, we’d divide the NOPAT by Capital Employed:
ROCE = $3,500 ÷ $20,000 = 0.175 or 17.5%
This means that for every dollar ABC invests in its business operations, it earns a return of 17.5%.
What factors affect the Return on Capital Employed?
The following factors affect the Return on Capital Employed:
1. Operating Efficiency:
A company’s operating efficiency is a major driver of its Return on Capital Employed. The more efficiently the firm operates, the higher the Return on Capital Employed will be.
2. Leverage:
Companies that use leverage in the form of debt to finance their operations can create higher returns on capital employed. This is because the interest on the debt increases return but does not affect the cost structure of the company, resulting in a larger return for each dollar invested by shareholders. However, this also means more risk for the company, as it is more exposed to interest rate fluctuations and higher levels of debt.
3. Dividend Policy:
Companies that pay out high dividends tend to have lower Return on Capital Employed than those with low dividend policies. This is because the payment of dividends reduces the amount of retained earnings available for reinvestment in the business, resulting in a lower return for each dollar of capital employed.
4. Tax Rates:
High tax rates can significantly reduce the amount of after-tax profit generated from the same investment, leading to a reduced Return on Capital Employed. Similarly, low tax rates can have a positive effect on returns.
5. Interest Rates:
Rising interest rates can have a negative effect on a company’s Return on Capital Employed, as the cost of debt financing increases. On the other hand, falling interest rates can reduce the cost of debt financing and increase returns.
6. Economic Conditions:
Economic conditions in an industry or region can have an impact on a company’s ability to generate profits and thus affect its Return on Capital Employed. If an industry is in decline or if a region is suffering from the economic downturn, returns tend to be lower.
7. Asset Utilization:
The more efficiently assets are used, the higher the return on capital employed will be. Therefore, companies need to ensure that they use their assets in the most efficient way possible to maximize returns. This includes factors such as the quality of plant and equipment, workforce utilization and asset optimization.
8. Cost Structure:
The cost structure of a company has a direct impact on its Return on Capital Employed. Companies with high costs relative to their revenue will tend to have lower returns than those with low costs. Therefore, companies should strive to maintain a cost structure that allows them to remain competitive while still generating returns for shareholders.
These are some of the key factors that affect a company’s Return on Capital Employed and should be considered when making investment decisions.
What is a good Return on Capital Employed?
A good return on capital employed (ROCE) is an important measure of profitability and financial performance. It is a ratio that measures the amount of profit generated by a company in comparison to the amount of money invested into the business, or capital employed.
The higher this ratio, the more profitable a company is – it indicates that it has the capacity to generate profit from the capital it has tied up in its operations. Generally, a good ROCE is one that is higher than the company’s cost of capital or its weighted average cost of capital (WACC). This indicates that a company is making more money than it needs to service its debt and equity investments. Additionally, a high return on capital employed can also indicate that the company is making efficient use of its resources.
What are examples of Return on Capital Employed?
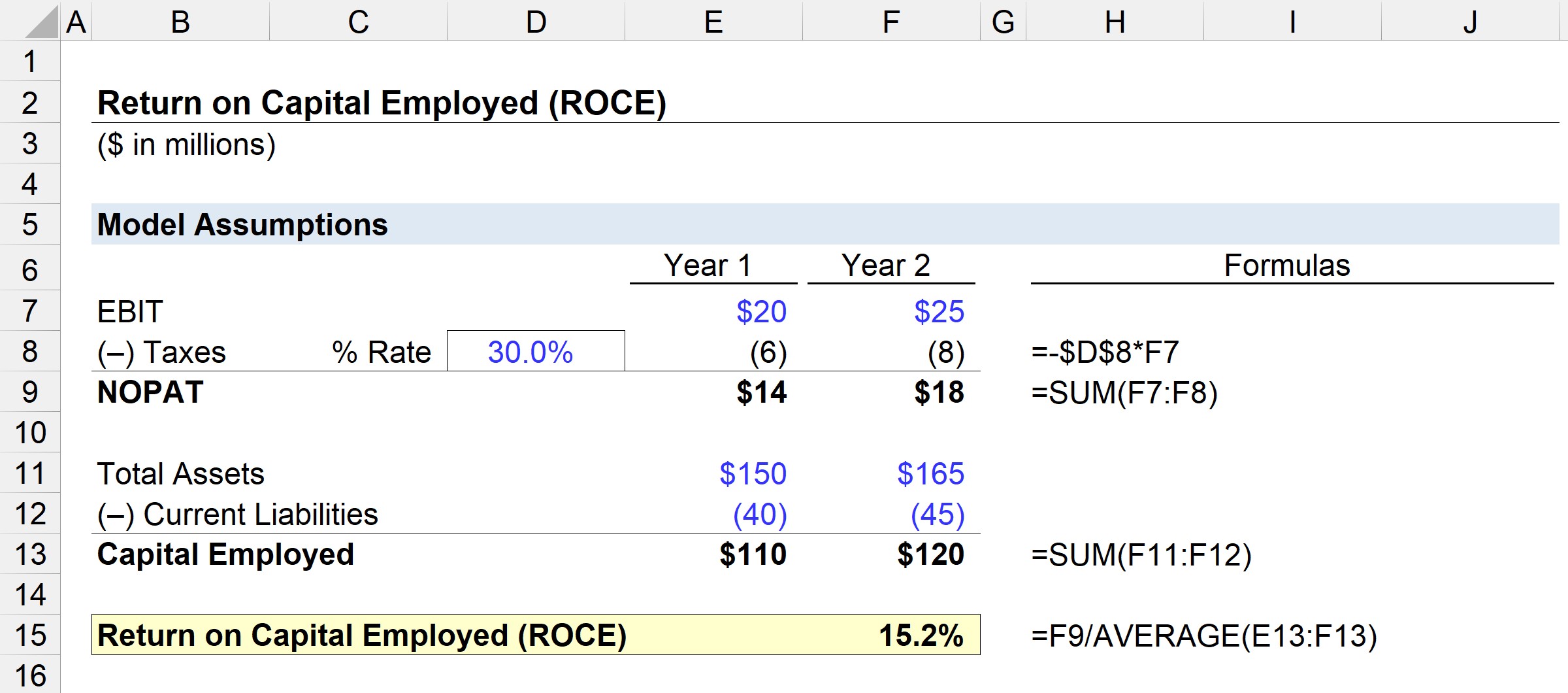
Using the assumptions of a 30% tax rate for both periods, we can calculate NOPAT (Net Operating Profit After Tax) by multiplying EBIT (Earnings Before Interest and Taxes) by one minus the tax rate assumption.
For this example, Year 1 would be $14 million (20 million x (1 – 30%), while Year 2’s NOPAT would be $18 million (25 million x (1 – 30%)). Capital employed is equal to total assets minus current liabilities. For Year 1, the capital employed is $110 million ($150 million – $40 million) and for Year 2 it is $120 million ($165 million – $45 million).
Using these figures in the ROCE formula, the example company’s ROCE comes out to 15.2%. This means that for every $10 of capital employed, profits of $1.52 are returned – which can be compared to industry peers and historical periods to determine if management is efficient at capital utilization.
EXAMPLE 2:
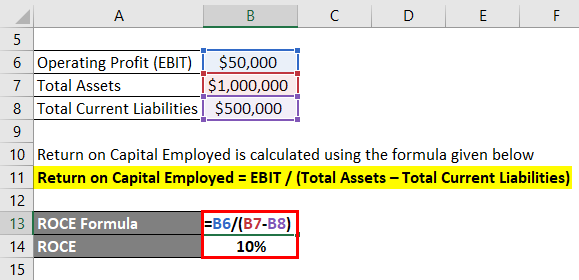
The company’s performance in the past year can be assessed by computing its Return on Capital Employed (ROCE). This ratio is calculated as follows:
ROCE = EBIT / (Total Assets – Total Current Liabilities).
In this example, the reported operating profit was $50,000, and total assets and total current liabilities stood at $1,000,000 and $500,000 respectively as reported in the balance sheet. This yields a ROCE of 10%, which indicates that the company generated a return on capital employed of 10% during the year. Thus, we can conclude that the company’s performance in the past year was satisfactory.
Tips to improve the Return on Capital Employed
following strategies can help to improve the Return on Capital Employed :
1. Increase operational efficiency:
Companies should focus on increasing the efficiency of their operations and processes so that they can produce more with less resources, leading to an improvement in their ROCE. This could involve streamlining production processes, reducing wastage and improving inventory management.
2. Reduce debt:
One way a company can improve ROCE is to reduce its debt. When a company has too much debt, it can be difficult to pay back creditors and make payments on time, reducing the amount of capital available for productive investments. Therefore, reducing debt can improve ROCE by freeing up more capital to invest in revenue-generating activities.
3. Invest in assets:
Companies should invest in new assets and technologies that can improve the efficiency of their operations. This could involve purchasing new equipment, investing in training for employees or upgrading existing systems. By investing in productive assets, companies can increase ROCE by improving the productivity of their capital.
4. Buy back shares:
Companies may also choose to buy back their own shares, which can reduce the amount of capital invested in the company. This reduces equity capital and increases ROCE, as profits are spread over a smaller number of shares
5. Improve pricing:
Companies should focus on improving their pricing strategy by charging higher prices for products and services that have high customer demand or that offer customers more value. This could involve introducing new pricing tiers or changing the way discounts are applied to products and services. By improving pricing, companies can increase their profits and improve ROCE.
6. Increase sales:
Finally, companies should focus on increasing sales by expanding into new markets or launching innovative products or services. By increasing the number of customers buying their products and services, companies can increase their profits, leading to higher ROCE.
By implementing these strategies, companies can improve their Return on Capital Employed (ROCE) and become more competitive in the market.
The Bottom Line
Return on Capital Employed (ROCE) is a financial ratio that measures the profitability of a company. It tells you how much profit a company generates for each dollar it invests in its business. A high ROCE means the company is generating a lot of profits and is, therefore, efficient. The guide provided should help you understand ROCE and how to use it when making investment decisions.

