One of the most important measures for any business is its profitability. Knowing your company’s operating profit margin (OPM) allows you to understand how efficiently it can generate revenue and cover its costs. By understanding your OPM, you will be better informed when making decisions about investments, mergers and acquisitions, pricing strategy, expense management…and more! In this in-depth blog post, we are going to explore what OPM is, and what factors affect it and dive into some strategies that businesses can implement to enhance their OPM. Whether you own or manage a business or look more closely at the performance of public companies these insights should prove useful! Let’s jump right in – our mission today: gain clarity on operational profit margins today so that you have the foundation necessary for future success!
What is the Operating Profit Margin?
The Operating Profit Margin is a measure of profitability that indicates how much profit a company makes after accounting for all of its operating expenses. This metric measures how efficient a company is at generating profit from its operations, and is used as an important indicator of a company’s financial health. Investors may look at this metric to determine whether a certain business is making money or not. It can also be used to compare profitability between different companies within an industry. By understanding the Operating Profit Margin, investors can better understand how a company is performing and make more informed decisions when considering investing in it.
The Operating Profit Margin can be a helpful tool for investors to use when evaluating different companies, as it provides an accurate measure of the profitability of each company’s operations. It allows them to compare one company against another and assess which is more profitable or efficient. Additionally, it can provide investors with insight into how well management teams are running their businesses and making decisions.
Why Is It Important For Startups to track the Operating Profit Margin?
Following are the reasons why tracking the Operating Profit Margin is important for Startups:
1. Evaluating Performance:
Operating Profit Margin can help startups to evaluate the performance of their operations by measuring how efficiently they are utilizing their resources and if they are successful in generating profits from these resources. It also provides startups with feedback on areas where they can improve and become more efficient.
2. Setting Goals and Objectives:
Tracking the Operating Profit Margin can help startups set realistic goals and objectives that are achievable within their budget. This will ensure that they are able to remain competitive in the market, while still achieving the desired profits.
3. Identifying Areas of Improvement:
By tracking the Operating Profit Margin, startups can identify areas where they need to make improvements in order to maximize their profits. This can help them make the necessary changes that are needed to increase their profitability and stay ahead of the competition.
4. Making Strategic Decisions:
Operating Profit Margin allows startups to make informed decisions about how to allocate resources among different areas of operations. This helps them prioritize expenditures and determine which investments will be most beneficial in the long run.
5. Comparing Performance and Benchmarking:
Tracking the Operating Profit Margin allows startups to compare their performance with that of their competitors in the same field or industry. This will provide them with valuable insights into how they can improve their operations and become more profitable.
Therefore, tracking the Operating Profit Margin is an important metric for startups as it helps them evaluate their performance, set realistic goals and objectives, identify areas for improvement, make strategic decisions and compare their performance with that of their competitors.
This ensures that they are able to remain competitive in the market while achieving maximum profits from their resources. By utilizing the Operating Profit Margin, startups can make informed decisions about their operations and ensure that they are maximizing their profits. This will help them remain competitive in the market and succeed in achieving long-term success.
How To Calculate the Operating Profit Margin?
Here is the formula to calculate the Operating Profit Margin:
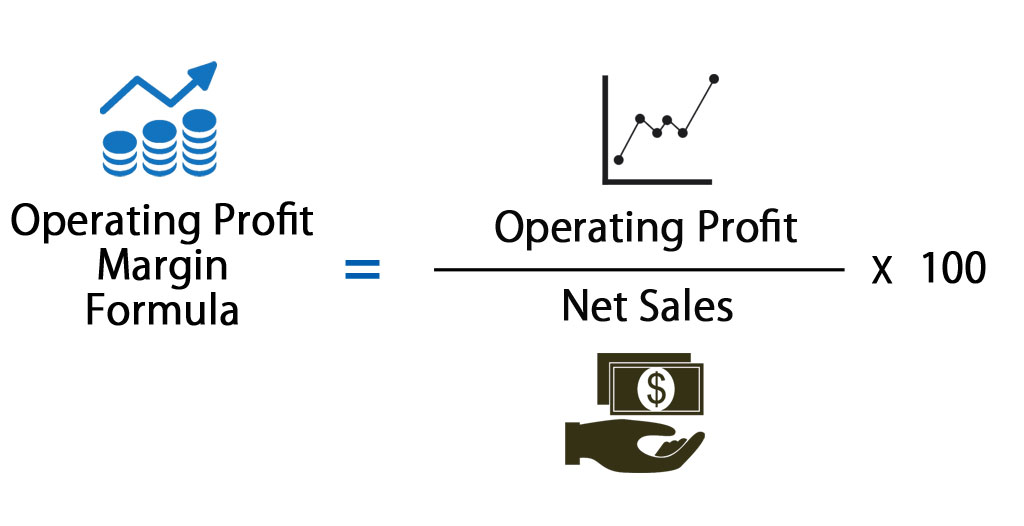
Let’s take an example to demonstrate how the formula works.
Suppose a company has total sales of $150,000 and its cost of goods sold add up to $60,000. The operating expenses are $50,000 and the interest
expense is $10,000.
To calculate the operating profit:
Net Operating Profit = Total Revenue – Cost of Goods Sold – Operating Expenses – Interest Expense
= 150,000 – 60,000 – 50,000 – 10,00
= 30,000
Now to calculate the operating profit margin:
Operating Profit Margin = (Net Operating Profit/Total Revenue)*100
= (30,000/150,000)*100
= 20%
Therefore, the company has an operating profit margin of 20%.
This means that for each dollar of revenue earned, it generates 20 cents in operating profit.
It is important to note that the operating profit margin can vary significantly from one industry to another.
What factors affect the Operating Profit Margin?
The following factors affect the Operating Profit Margin :
1. Revenue:
The amount of revenue generated by the company is an important factor that affects its Operating Profit Margin. Higher revenue will lead to higher operating profit margins, while lower revenue will lead to lower operating profit margins.
2. Cost of goods sold:
The cost of goods sold plays a major role in determining the Operating Profit Margin. Higher costs of goods sold will reduce the Operating Profit Margin, while lower costs of goods sold will increase it.
3. Expenses:
All other expenses incurred by the company such as research and development, advertising, employee wages, etc. can affect the Operating Profit Margin. If these costs increase, the Operating Profit Margin will decrease and vice versa.
4. Tax rate:
The tax rate also affects the Operating Profit Margin as a higher tax rate will reduce the total profit made by the company and thus lead to a lower Operating Profit Margin.
5. Interest rates:
Higher interest rates on loans taken by the company can also reduce its overall profits, leading to a lower Operating Profit Margin.
6. Inventory levels:
The amount of inventory held by the company can also affect its Operating Profit Margin. Higher inventory levels will lead to more expenses, and thus a lower Operating Profit Margin.
7. Leverage:
Companies that use more debt financing (leverage) to acquire assets or make investments will have lower Operating Profit Margins due to the interest payments on those debts.
8. Competition:
A company’s Operating Profit Margin can be affected by competition in the market. If there is more competition, prices may have to be lowered in order to compete and this can lead to a lower Operating Profit Margin.
9. Economy:
The overall economic environment can also affect the Operating Profit Margin of a company. In an economic downturn, there may be lower sales and cost pressures that can lead to lower Operating Profit Margins.
10. Cost structure:
The overall cost structure of a company will have an effect on its Operating Profit Margin. Companies with high overhead costs will have lower Operating Profit Margins compared to those with lower overhead costs.
11. Efficiency:
The efficiency of the company’s operations can also affect its Operating Profit Margin. Companies that are able to run their operations more efficiently will be able to generate higher profits and thus a higher Operating Profit Margin.
In conclusion, there are several factors affecting the Operating Profit Margin of a company and it is important for a company to consider these factors in order to maximize its profits.
What is a good Operating Profit Margin?
A good Operating Profit Margin depends on the industry and type of business. Generally, a higher Operating Profit Margin is always better because it indicates that the company is making more profits relative to its sales. A margin of around 10-15% is considered healthy in most industries, while anything above 20% is usually seen as exceptional.
However, this can vary significantly depending on the type of business and industry in which it operates. Ultimately, a good Operating Profit Margin should be one that provides a company with enough profits relative to its sales to sustain operations and reinvest in the business.
What is an example of Operating Profit Margins?
In order to calculate the operating profit margin of YOU Matter Inc., we need to begin by calculating the net sales. This can be done by subtracting the amount of sales returns from their gross sales, which is $564,000 – $54,000 = $510,000.
We then deduct the cost of goods sold from the net sales to arrive at the gross profit, which is $510,000 – $240,000 = $270,000. Finally, we subtract the labor expenses and general & administration expenses from this gross profit to get the operating profit: ($270,000 – $43,000 – $57,000) = $170,000.
From this number, we can calculate the operating profit margin using this formula: Operating Profit Margin = Operating Profit / Net Sales * 100. In this case, it would be $170,000 / $510,000 x 100 = 33.33%.
Therefore, the operating profit margin of YOU Matter Inc. is 33.33%
Tips to improve the Operating Profit Margin
The following strategies can help to improve the Operating Profit Margin:
1. Improve operational efficiency:
Identify and eliminate inefficiencies within operations. Pinpoint processes that take too long, require unnecessary steps or produce excess waste. Streamline processes for improved productivity and profitability.
2. Cut costs:
Review all expenses to identify where cost reduction is possible. Look for areas such as overhead costs, labour, materials, and other resources. Negotiate better prices with suppliers, review customer contracts for potential savings, and invest in infrastructure to improve efficiency.
3. Increase pricing:
If you can increase the price of your product or service without losing customers then this may be a viable option for improving profits. Carefully evaluate customer trends and competitor strategies to determine the best pricing strategy.
4. Increase sales:
Focus on increasing your sales volume in order to increase profits. Analyze customer trends, invest in marketing, and focus on customer retention activities to boost revenues.
5. Invest in technology:
Updating existing technologies or investing in new ones can help improve operational efficiency and reduce costs over time. Automation, cloud computing, and other new technologies can reduce the amount of time, resources, and manual labour required for certain tasks.
6. Outsource:
Consider outsourcing non-core business activities to third parties in order to save on costs and increase efficiencies. For example, outsourcing customer service or logistics operations rather than managing them in-house
7. Manage inventory:
Effective inventory management is essential for minimizing costs and keeping operations running smoothly. Monitor stock levels, optimize purchase orders, and redeploy excess resources to manage inventory effectively.
8. Negotiate credit terms:
Review customer payment terms with suppliers and vendors in order to make sure you’re getting the best deals possible. Aim for longer payment terms and better discounts, if possible.
9. Increase asset turnover:
Aim to increase the number of times that assets are used within a given period by increasing the sales volume and reducing the amount of time it takes for each sale.
10. Reduce financing costs:
Negotiate with lenders for more favourable interest rates and credit terms in order to reduce financial costs. Pay down debt and consider refinancing options to improve profitability.
By implementing these strategies, businesses can improve their operating profit margin and maximise their profits.
Wrap Up
The operating profit margin is a simple, but important ratio. By understanding what it measures and how to calculate it, you can get a clear picture of your company’s profitability. You can use the operating profit margin to compare your company’s performance over time or against other companies in your industry.

