Gross profit is an essential figure when it comes to understanding the financial performance of any business. Understanding your gross profits gives insight into the efficiency of operations, and allows you to assess whether or not products are being successfully marketed and sold at profitable margins. Knowing your gross profits can help inform decision-making around product pricing, inventory management, marketing strategies, and capital investments – just to name a few! In this blog post, we’ll be exploring all there is to know about gross profits; from how they’re calculated and reported on financial statements to different techniques for managing them effectively.
What is Gross Profit?
Gross profit is a measure of how much an organization has earned after deducting the cost of goods sold from its revenue. It is a metric for business profitability and is typically expressed as a percentage or dollar amount. Gross profit does not account for other expenses such as administrative costs, interest payments, taxes, and depreciation – these are accounted for in the company’s net profit or earnings.
Gross profit is a helpful metric for business owners to quickly gauge their profitability and make decisions about pricing, inventory management, and overall financial performance. Gross profit is not only an important indicator of financial performance, but it is also a key measure used for evaluating business success. It helps investors and lenders judge the current and potential profitability of a company, which can influence decisions such as whether to invest in or loan money to a business.
Why Is It Important For Startups To track the Gross Profit?
Following are the reasons why startups need to track the gross profit:
1. Increased Visibility:
Tracking gross profit helps startups to monitor their financial performance in real-time and identify areas where improvements can be made. This visibility helps them make more informed decisions and achieve better financial results over the long term.
2. Enhanced Cash Flow Management:
By tracking gross profit, startups can have a better handle on their cash flow. This can help them make informed decisions about how to allocate their resources and manage their expenses.
3. Improved Investor Relations:
Tracking gross profit also helps startups build better relationships with investors. Investors are often interested in the startup’s financial track record, which can be demonstrated through tracking gross profit.
4. Greater Efficiency:
Tracking gross profit helps startups to become more efficient in their operations. By understanding their total costs, they can better manage their resources and reduce waste.
5. Improved Decision Making:
Finally, tracking gross profit helps startups make more informed decisions about how to allocate resources and where to invest capital. This enables them to maximize the potential of their business and optimize their performance.
6. Reduced Risk:
Having visibility into gross profit can help startups identify potential risks and make strategic changes to improve their financial health. By monitoring their financial performance, they can take proactive steps to reduce risk and ensure the success of their business.
7. Financial Forecasting:
Tracking gross profit also helps startups to have a better view of their current and future financial performance. This enables them to make informed decisions about their strategy and budgeting, as well as plan for the future based on past trends.
8. Increased Accountability:
Finally, tracking gross profit can help startups hold themselves more accountable. By monitoring their financial performance, they can identify any issues and take corrective action to prevent them from recurring. This ensures that they remain on track toward achieving their goals and objectives.
In conclusion, tracking gross profit is an important part of managing a startup’s finances. By understanding their financial position more clearly, startups can make better decisions and improve their overall performance in the long term.
How To Calculate the Gross Profit?
Here is the formula to calculate the Gross profit:
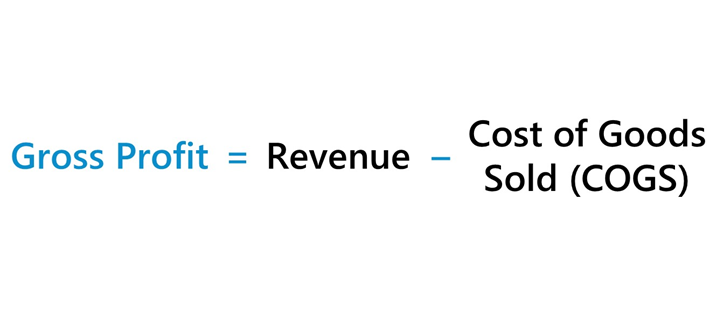
To calculate gross profit, simply take the total revenue and subtract the Cost of Goods Sold. For example, if a company had $10,000 in total revenue and $6,000 in COGS, the gross profit would be $4,000.
What factors affect the Gross Profit?
The following factors affect gross profit:
1. Revenues:
The revenues earned from a business’s sales and services are the most significant factor that affects gross profit. Higher revenues mean higher gross profits, while lower revenues can decrease them significantly.
2. Cost of Goods Sold (COGS):
This is the amount paid for raw materials or finished goods used in manufacturing and is a major factor in determining the gross profit. Higher COGS means lower gross profits, while lower COGS can increase them significantly.
3. Selling and Administrative Expenses (S&A):
These expenses include salaries, office supplies, advertising, and other overhead costs associated with running a business. They play an important role in calculating gross profit as higher S&A means lower gross profits, while the opposite holds true as well.
4. Interest Expense:
This is the cost of borrowing money to finance a business’s operations and it affects gross profit because higher interest expenses mean lower gross profits.
5. Depreciation Expense:
This is the amount of money charged as a reduction in value for an asset used in a business, such as machinery and equipment. Higher depreciation expenses mean lower gross profits, while the opposite holds true as well.
6. Taxes:
Any taxes owed to the government must be paid from the gross profit of a business, which can significantly reduce it.
7. Discounts:
If a business offers discounts on its products or services, this can affect the gross profit as well. Discounts reduce the amount of money earned from sales, resulting in lower gross profits.
8. Price:
The price of a product or service directly affects the gross profit margin because higher prices mean higher gross profits and vice versa.
9. Volume of Sales:
The number of products or services sold is also a factor in determining the gross profit margin. Higher volumes of sales mean higher gross profits, while lower volumes can decrease them significantly.
Overall, these factors affect the gross profit of a business by either increasing or decreasing it significantly. Knowing how to manage these factors effectively is key to achieving and maintaining high levels of profitability for any business.
Quotes about Gross Profit?
“Gross profit is what’s left when you subtract the cost of goods sold from sales revenue—it is your money to do with as you please.” – Robert Kiyosaki
“Gross profit is one of the most important measures in any business. It tells us how well a company manages costs while still driving sales.” – Tim Berry
“Gross profit is the lifeblood of any business. If it’s not healthy, the company won’t survive.” – Jeff Weber
“Gross profit is the foundation upon which successful businesses are built and sustained over time.” – John Gardner
What is a good gross profit?
A good gross profit will depend on a variety of factors, including how much money you can invest in your business, the types of services or products you are offering, and the market you are operating in.
Generally speaking, a healthy gross profit margin should generally be around 20-40%. However, it is important to keep in mind that this number will vary from business to business and industry to industry.
Ultimately, you should strive for a gross profit that is in line with the expectations and needs of your particular market. It is important to consider all factors when determining what is a good gross profit for your company.
What is an example of Gross Profit?
| Revenues | (in USD millions) |
| Automotive | 141,546 |
| Financial services | 10,253 |
| Other | 1 |
| Total revenues | 151,800 |
| Costs and expenses | |
| Automotive cost of sales | 126,584 |
| Selling, administrative, and other expenses | 12,196 |
| Financial Services interest, operating, and other expenses | 8,904 |
| Total costs and expenses | 147,684 |
Company ABC’s income statement can be used to calculate the gross profit and the gross profit margin. The total revenue is USD 151,800 million. The cost of goods sold is USD 126,584 million, while selling, administrative and other expenses are mostly fixed costs. By subtracting the cost of goods sold from revenues, a gross profit of USD 25,216 million is obtained.
Example 2:
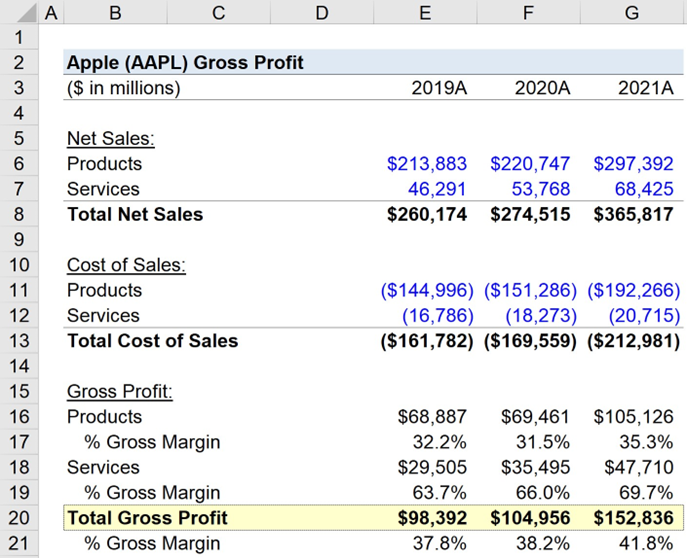
Let us consider that In our model, we’ll separately calculate the gross profit and gross margin metrics for the products and services division. The Products Gross Profit was $68,887 million (32.2% Gross Margin) in 2019A, $69,461 million (31.5% Gross Margin) in 2020A, and $105,126 million (35.3% Gross Margin) in 2021A, respectively.
Meanwhile, the Services Gross Profit was $29,505 million (63.7% Gross Margin) in 2019A, $35,495 million (66.0% Gross Margin) in 2020A, and $47,710 million (69.7% Gross Margin) in 2021A, respectively.
The differences in gross margins between products and services were 32%, 35%, and 34%, reflecting how services are much more profitable than physical products.
Finally, we’ll calculate the total gross profit and gross margin of Apple which combines the profits (and margins) of both the product and services divisions. The total gross profit was $98,392 million (37.8% Gross Margin) in 2019A, $104,956 million (38.2% Gross Margin) in 2020A, and $152,836 million (41.8% Gross Margin) in 2021A respectively.
From 2019 to 2021, Apple’s gross margin averaged approximately 39%, but it is heavily weighed down by the products division.
Tips to Increase the Gross Profit
Following are some Strategies to Increase the Gross Profit:
1. Reassess the cost structure:
The first step towards improving gross profit is to reassess your current cost structure. Review all aspects of your business and identify areas where you can make cost reductions or increase efficiency. This could include reducing overhead costs, renegotiating supplier agreements, improving inventory management systems, exploring alternative production methods and technologies, and reducing waste.
2. Increase prices:
Raising your prices is an obvious way to increase gross profit margin, as long as you don’t price yourself out of the market or lose customers because of it. Consider carefully which products and services you want to raise prices for and how much to charge for them.
3. Introduce new products or services:
If you can’t raise prices, consider introducing a new product or service to your lineup. Ensure that this product or service is in demand and can be priced higher than existing items.
4. Focus on marketing:
Marketing effectively can help boost gross profit margins by drawing in more customers, which can result in more sales. Investing in marketing will help increase your customer base, brand awareness, and loyalty, which can all help to drive up gross profits.
5. Implement, a customer rewards program:
Loyal customers are a great way to boost profits as they are more likely to purchase from you and spend more money than new customers. Consider introducing a rewards or loyalty program for your customers to encourage repeat purchases.
6. Build relationships with suppliers:
Establishing long-lasting relationships with suppliers can help you negotiate better prices and discounts. This can result in lower costs, which will ultimately increase gross profits.
7. Increase operational efficiency:
Streamline your operational processes by reducing waste and increasing efficiency throughout your business. Implementing new technologies or processes can help to speed up production, which can also increase gross profits.
8. Focus on customer service:
Good customer service is essential for increasing sales and building a loyal client base. Ensure that you are delivering top-notch customer service at all times to increase customer satisfaction levels, which will in turn result in more sales and higher gross profits.
9. Improve pricing strategies:
Re-evaluate your current pricing strategies to ensure that they are working as intended. Make sure you are correctly balancing the cost of goods with market prices to maximize profits.
10. Monitor performance:
Regularly review how your business is performing, so you can pinpoint any areas that need to be improved to increase profits. Benchmarking against competitors can also help you identify areas where your business is lagging and make the necessary adjustments.
These strategies can help your business increase gross profits, allowing you to reinvest that money into other areas of your business or save it for a rainy day.
Wrap-Up:
If you’re not paying attention to your gross profit, you could be making some serious that go into calculating it, and always keep an eye on it. With a little bit of effort, you can use the gross profit to make smart decisions for your business and ensure its success

