If you’re a business owner, you know that keeping an eye on your gross profit margin is essential. But what is the gross profit margin? And why is it so important? This guide will explain everything you need to know about gross profit margin and how to protect and improve yours. So read on to learn more!
What Is A Gross Profit Margin?
A gross profit margin is a financial metric used to assess a company’s financial health and profitability. It’s one of three major profitability ratios, the others being operating profit margin and net profit margin.
The gross profit margin measures the revenue a company retains after subtracting the cost of goods sold (which can include labor, materials, and other direct production costs).
The higher the gross profit margin, the more profitable a company is. Many investors use the gross profit margin to assess a company’s financial health.
A high gross profit margin indicates that a company is efficient at generating revenue and keeping expenses low.
A low gross profit margin, on the other hand, may indicate that a company is struggling to generate revenue or keep expenses under control.
Why Is A Gross Profit Margin Important For a Startup?
Gross profit margin is essential for business because it is one of the key indicators of a company’s financial health. It is a good way to measure a company’s profitability and compare it with other companies in its industry.
A gross profit margin is also an important tool for management, as it can help them assess the efficiency of the business and identify areas where improvements can be made.
For example, Company A has $1 million in revenue and $600,000 in COGS. Its gross profit margin would be 40% because 40% of its revenue ($400,000) is left over after paying for its COGS.
Meanwhile, Company B also has $1 million in revenue, but its COGS are $800,000. Its gross profit margin would be 20% because only 20% of its revenue ($200,000) is left over after paying its COGS.
So even though both companies have the same amount of revenue, Company A is in a better financial position than Company B because it has a higher gross profit margin.
A high gross profit margin is only sometimes possible or desirable, though. The pricing strategy and competition will ultimately drive how the margin reacts to consumer buying habits. For example, if everyone in your market sells products at low margins, you might have to do the same to stay competitive and generate sales.
The goal is to capture the highest possible margin without sacrificing sales or compromising your company’s profitability. By closely monitoring your gross profit margins, you can get a good sense of your company’s overall financial health and make informed decisions about pricing, product mix, and other factors affecting your bottom line.
How To Calculate Gross Profit Margin?
There are a few different ways to calculate gross profit margin, but the most common is to take your total revenue and subtract your cost of goods sold. This will give you your gross profit, which you can divide by your total revenue to get your gross profit margin.
Here’s the formula:
Total Revenue – Cost Of Goods Sold / Total Revenue × 100 = % Gross Profit Margin
For example, if your company had total revenue of $100,000 and a cost of goods sold of $40,000, your gross profit would be $60,000. Divided by total revenue, this gives you a gross profit margin of 60%.
Generally speaking, a higher gross profit margin is better, as it indicates that your company is making more money on each sale. However, there are some industries where a lower gross profit margin is perfectly normal, so it’s essential to put your gross profit margin in context.
What Is A Good Gross Profit Margin?
It is difficult to determine whether or not a business has achieved a good profit margin as it varies across different industries. While the overall average is above 30%, there is still a wide disparity in gross profit margin between the automotive business (9.04%) and regional banks (99.75%), for instance.
Generally, service industries that don’t sell physical products will have higher gross profit margins because they have a much lower cost of goods sold. A consultant or lawyer, for example, will not have as many expenses to meet when providing clients with their “goods.”
In comparison, the manufacturing and food vendors must have higher upfront costs for equipment and raw materials to deliver purchasers a well-finished product.
A good gross profit margin, according to investors in startups, is one that is above 50%. This means that the company has enough excess profit after paying for production costs to cover other expenses, such as salaries, rent, and marketing. Anything below 50% may be a sign that the company is not doing well financially.
Using different industries as a base, we will determine whether or not a business has achieved a good gross profit margin. Below are some averages for different industries as of January 2021, including their net profit margins.
| Industry | Gross Profit Margin | Net Profit Margin |
| Advertising | 23.99% | 0.34% |
| Apparel | 49.77% | -3.94% |
| Auto and Truck | 9.04% | 1.4% |
| Banks (Regional) | 99.75% | 23.79% |
| Building Materials | 28.38% | 5.06% |
| Computer Services | 27.16% | 3.62% |
| Home Furnishings | 27.03% | 4.63% |
| Healthcare Products | 56.94% | 10.91% |
| Household Products | 50.87% | 11.71% |
| Machinery | 34.50% | 6.58% |
| Packaging and Container | 22.39% | 2.98% |
| Precious Metals | 50.17% | 15.79% |
| Recreation | 37.58% | -2.12% |
| Restaurants and Dining | 27.60% | 5.69% |
| Retail (General) | 24.27% | 2.79% |
| Retail (Online) | 42.53% | 4.95% |
| Software (Internet) | 58.58% | -5.60% |
| Transportation | 19.91% | 3.88% |
| Total Market* | 36.22% | 5.05% |
Total Market calculations include the industries that are not shown.
Example Of Gross Profit Margin
For the fiscal year ending September 30th, 2017, Apple reported total revenue of $229 billion and COGS ($141B) as shown from their 10K statement below.
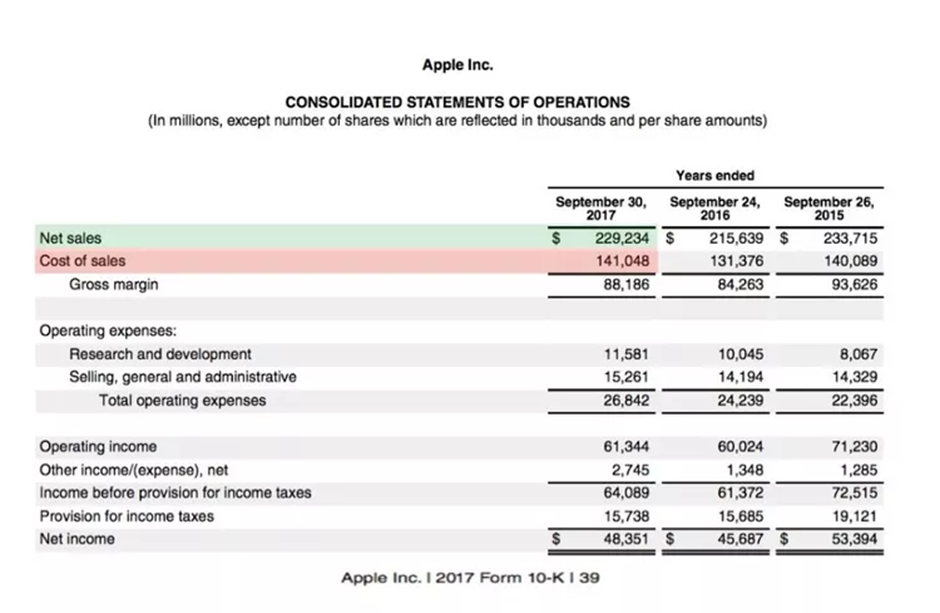
The gross profit margin for 2017 was 38%. Using the formula, it would be calculated as follows:
($299B – $141B) / $299B × 100 = 38%
This concludes that for every dollar Apple generated in sales, the company got 38 cents as gross profit before paying other business expenses.
Factors That Can Affect A Company’s Gross Profit Margin
A company’s gross profit margin is one of the most important indicators of its financial health. Some factors can affect a company’s gross profit margin.
Type of products or services
One of the most important factors is the type of products or services the company sells. A company selling high-end products or services will typically have a higher gross profit margin than a company that sells lower-end products or services. This is because high-end products or services generally have a higher price point, which allows the company to generate more revenue per sale.
Cost of goods sold
Another important factor affecting a company’s gross profit margin is the cost of goods sold. If a company’s costs are high, it will have a lower gross profit margin. This is because a higher cost of goods sold means a company has to keep more revenue to cover these costs. Higher costs can be caused by several factors, such as raw materials, labour, or shipping costs.
Price
Finally, the price of a company’s products or services can also affect its gross profit margin. If a company raises its prices, it will typically see a corresponding increase in its gross profit margin. This is because the company will be able to generate more revenue per sale.
Conversely, if a company lowers its prices, it will typically see a decrease in its gross profit margin. This is because the company will have to generate less revenue per sale to cover its costs.
These factors are important to consider when evaluating a company’s gross profit margin. By understanding how these factors can affect the margin, investors can get a better sense of the company’s financial health.
Strategies Businesses Can Use To Improve Their Gross Profit Margins
As any business owner knows, gross profit margins are essential to profitability. There are several strategies businesses can use to improve their gross profit margins. Some of them are:
Increase prices
One of the most obvious ways to improve your gross profit margin is to increase your prices. If you’re selling a product for $100 and it costs you $50 to produce, then your gross profit margin is 50%. If you increase the price of the product to $120, then your gross profit margin becomes 60%.
Of course, there’s a risk that you’ll price yourself out of the market if you increase your prices too much. But as long as you research and ensure that your prices are still competitive, then raising prices can be a good way to improve your gross profit margin.
Improve efficiency
Improving your business’s efficiency is another way to decrease costs and improve your gross profit margin. If you can find a way to produce the same amount of product with less labour, you’ll be able to reduce your costs and increase your gross profit margin.
There are some ways to improve your business’s efficiency, such as investing in new technology, streamlining your manufacturing process, or hiring more efficient employees.
Sell higher-margin products
If you sell a mix of products, then you might be able to increase your gross profit margin by selling more of the higher-margin products and less of the lower-margin products.
For example, suppose you sell two products: Product A has a 50% gross profit margin, and Product B has a 40% gross profit margin. If you sell equal amounts of each product, your overall gross profit margin will be 45%. But your gross profit margin will increase if you sell more of Product A and less of Product B.
Bundle products together
Another way to sell more high-margin products is to bundle them.
For example, you sell a software program for $100 and a training course for $200. If you sell them separately, your gross profit margin on the software is 50%, and your gross profit margin on the training course is 60%. But if you bundle them together and sell them for $250, your gross profit margin on the bundle will be 70%.
Focus on high-value customers
If you have a mix of high-value and low-value customers, you can increase your gross profit margin by focusing on the high-value customers.
For example, let’s say you have two types of customers: Type A spends $10,000 per year, and Type B spends $1,000 per year. If you have equal numbers of each type of customer, your gross profit margin is 10%. But if you focus on Type A customers and increase your market share with them to 60%, your gross profit margin will increase to 15%.
Technology
Tech can be a powerful tool for improving your gross profit margin. There are many ways that technology can help, such as reducing costs, increasing efficiency, or improving your product.
For example, assume you sell a physical product. If you use technology to automate your manufacturing process, you’ll be able to reduce your costs and increase your gross profit margin.
Wrap Up
By increasing your gross profit margin; you allow your business to make more money while also becoming more stable. While there are several ways to increase your gross profit margin, they all come down to one thing: improving your bottom line. Thanks for reading, and we hope this guide helped understand why gross profit margin is essential for businesses.

