Are you looking for a better way to make smart investments with your capital? If so, understanding the concept of the capital consumption ratio is essential. Capital consumption ratio helps you assess whether or not an investment is worthwhile by comparing the return you get on it versus its cost. This guide provides a comprehensive view of what capital consumption ratio is and how it impacts your decisions as an investor. From defining this important financial tool to walking through examples, we’ll provide all the insight needed to maximize returns while minimizing risks when investing money.
What is Capital Consumption Ratio?
Capital Consumption Ratio (CCR) looks at how much capital has been consumed for every dollar of annual revenue receivable (ARR) achieved. This will give you the best assessment of where you stand with your business and whether there is enough excess capital to invest in growth rather than maintain operations.
CCR measures the total cumulative amount of equity raised and debt drawn compared to the amount of cash available in the accounts as indicated on the balance sheet; this figure is adjusted according to any dividends/distributions made throughout its lifespan. By monitoring changes in CCR over time, you can more accurately estimate how much capital is required to make a certain move or invest in an initiative for growth going forward.
Why Is It Important For Startups To Track Their Capital Consumption Ratio?
Making sure that startups are utilizing their capital to its fullest potential is essential for long-term success. Tracking a startup’s Capital Consumption Ratio can provide valuable insight into how funds are being allocated, and help identify areas of potential waste or inefficiency.
Along with reducing costs, understanding the relationship between capital and output can assist a startup in making more informed decisions when allocating resources, ensuring that the limited capital available is used to generate maximum return and growth.
This kind of analysis helps startups gain visibility into their existing financial health, and create stronger strategies for long-term sustainability. For these reasons, it is important for startups to track their Capital Consumption Ratios – an invaluable tool in creating value and staying competitive.
How do you calculate the Capital Consumption Ratio?
Capital Consumption Ratio = Total cumulative capital consumed/ARR achieved
The Capital Consumption Ratio is a metric that measures how rapidly capital is consumed throughout a project. It is calculated by dividing the total cumulative capital consumed over the life of the project by the Annual Rate of Return (ARR) achieved for each period. This ratio provides insight into how efficiently capital has been managed and consumed.
A high ratio means that too much capital was used to generate a given level of return, while a low ratio provides evidence of efficient use of resources. It also helps demonstrate how much investments have grown in relation to their initial cost. Monitoring the Capital Consumption Ratio is an essential part of ensuring that all invested capital is used in an efficient and productive manner, creating positive returns for stakeholders in the long term.
What factors affect Capital Consumption Ratio?
The factors that affect the capital consumption ratio:
The type and quality of capital used
The use of more sophisticated capital equipment (such as computer-controlled machinery) will generally result in a higher CCR than simpler machines.
Utilization rate
The greater the utilization rate of a piece of equipment, the higher its CCR is likely to be.
Economic conditions
During periods of recession and slow growth, businesses may be more likely to invest in less expensive capital equipment that is less efficient but more affordable.
Technological progress
Newer technologies can often increase the efficiency and lifespan of capital goods, resulting in a higher CCR.
Labor costs
If labor costs are high, businesses may be more likely to invest in capital equipment that can replace human workers and reduce labor costs.
Intensity of competition
Firms operating in competitive markets may be more likely to invest in higher quality capital goods and upgrade existing equipment, resulting in a higher CCR.
Geographic location
Businesses located in regions with greater access to capital investments and more advanced technology may have a higher CCR than businesses in more remote areas.
Government regulations
Laws and policies that affect the cost of capital equipment can influence a firm’s CCR.
Tax incentives
Certain tax credits and deductions may encourage firms to invest in more efficient capital equipment, resulting in a higher CCR.
Financial leverage
The greater the amount of debt or other financial leverage used by a business, the higher its CCR will be.
Overall, these factors can significantly influence a firm’s capital consumption ratio and have an impact on its profitability and long-term success. By understanding and managing these factors, businesses can ensure that their CCR remains in line with their overall strategic objectives.
Why is Capital Consumption Ratio important?
The capital consumption ratio provides a useful metric for measuring the performance of an economy. It calculates the rate at which capital is being consumed, allowing us to track tangible assets such as buildings and infrastructure that are being used up to produce goods and services. Understanding this ratio allows us to determine how efficiently resources are being allocated and if production can be increased in certain areas of the economy.
It also tells us if current levels of investment are enough to sustain economic growth in the long run, so governments can plan sensibly for future growth. Ultimately, capital consumption ratio is a powerful indicator of economic performance that helps inform policymakers’ decisions on vital issues like infrastructure development and social welfare spending.
What are the effects of the Capital Consumption Ratio on a startup?
Here are the effects of the capital consumption ratio on a startup:
Reduced Profit Margins
A high capital consumption ratio means that a startup is spending more to generate income than its competitors, thereby reducing its profit margins and making it harder for them to turn a consistent profit.
Increased Business Risk
Since the capital consumed must be paid back by profits, startups with higher capital consumption ratios are more likely to fail as they would need to generate more profits to stay afloat.
Reduced Cash Flow
A higher capital consumption ratio means that the startup is spending more upfront for investments, which reduces their cash flow and makes it harder for them to execute their business plans.
Inability to Scale Quickly
A high capital consumption ratio means that the startup is spending a lot of money upfront, which limits their ability to scale quickly and efficiently.
Difficulties Accessing Financing
Startups with higher capital consumption ratios are more likely to be viewed as risky investments by lenders, making it difficult for them to access financing and grow their business.
Overall, the capital consumption ratio is an important factor to consider for any startup. It can have a major impact on their ability to generate profit and access financing, so startups should always be mindful of how much they are spending on investments compared to their competitors. By keeping careful track of their capital consumption ratio and taking steps to reduce it, startups can ensure that they remain competitive and profitable.
What is a good Capital Consumption Ratio?
A good capital-consumption ratio helps create a healthy and sustainable growth rate in an economy. A ratio much lower than one, such as 0.5, indicates that the output is not growing at a healthy rate; too few new investments are being made and as a result, the actual output will suffer in the long run.
On the other hand, a ratio higher than 1.0 could mean potential risks of increasing debt levels, which is unsustainable for any economy. For these reasons, it is important to maintain an optimal capital-consumption ratio so that both production and output can be sustained over time. If kept at the right level, this ratio has proved to be very effective at helping economies remain competitive and grow.
What are examples of Capital Consumption Ratio?
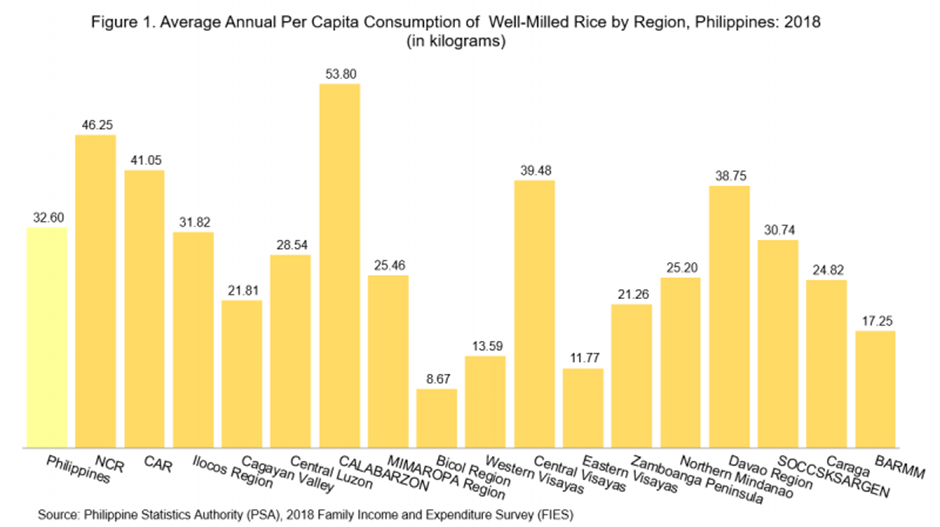
The 2018 Family Income and Expenditure Survey (FIES) revealed that the country’s annual per capita consumption of well-milled rice averaged 32.60 kilograms in 2018, but this number varied greatly among different regions. Region IV-A (CALABARZON) had the highest per capita consumption at 53.80 kilograms while National Capital Region (NCR) came close behind at 46.25 kilograms. Unfortunately, two regions experienced far lower than average levels of rice consumption; Region V (Bicol Region) had a per capita consumption of just 8.67 kilograms while Region VIII (Eastern Visayas) had an even lower 11.77 kilograms. It is crucial to understand and improve these gaps in order to ensure that all Filipinos have access to nutritional sustenance regardless of region or economic class.
How To Improve Capital Consumption Ratio?
Here is how you can improve your capital consumption rate:
Track your capital expenditures closely:
It’s important to carefully monitor and analyze your capital expenses on a regular basis. This allows you to identify any trends or problems that may be impacting the rate of consumption, so you can take corrective action if needed.
Invest in technology and automation
Investing in new technology and automation can help you become more efficient with the resources you have. This can result in cost savings, which will increase your capital consumption rate.
Leverage alternative financing sources
Consider using alternative financing sources such as leasing or debt instruments to replace large capital expenditures. This can help you spread out your costs over a longer period of time, allowing you to reduce your capital consumption rate.
Invest in maintenance and repairs
Regular maintenance and repairs can help extend the life of your assets, which means you don’t need to replace them as often. If you invest in regular preventive maintenance, it could lead to significant long-term savings in terms of capital consumption.
Use capital more efficiently
When implementing a new project or initiative, consider ways to use the resources you do have more effectively. This can help ensure that you’re not wasting money on unnecessary expenditures and improve your capital consumption rate in the long run.
By following these tips, you should be able to improve your capital consumption rate and enjoy the long-term benefits of cost savings.
Conclusion
The Capital Consumption Ratio is a powerful tool that can help guide your investment decisions. By understanding how it works and what factors influence it, you can make informed choices about where to allocate your resources. We hope this comprehensive guide has given you the information you need to get started using the CCR in your own analysis.

